Near miss: diver’s umbilical snagged by work basket during recovery to surface
- Safety Flash
- Published on 11 April 2018
- Generated on 29 April 2025
- IMCA SF 08/18
- 5 minute read
Jump to:
A diver’s umbilical became snagged on a tool basket during recovery.
What happened?
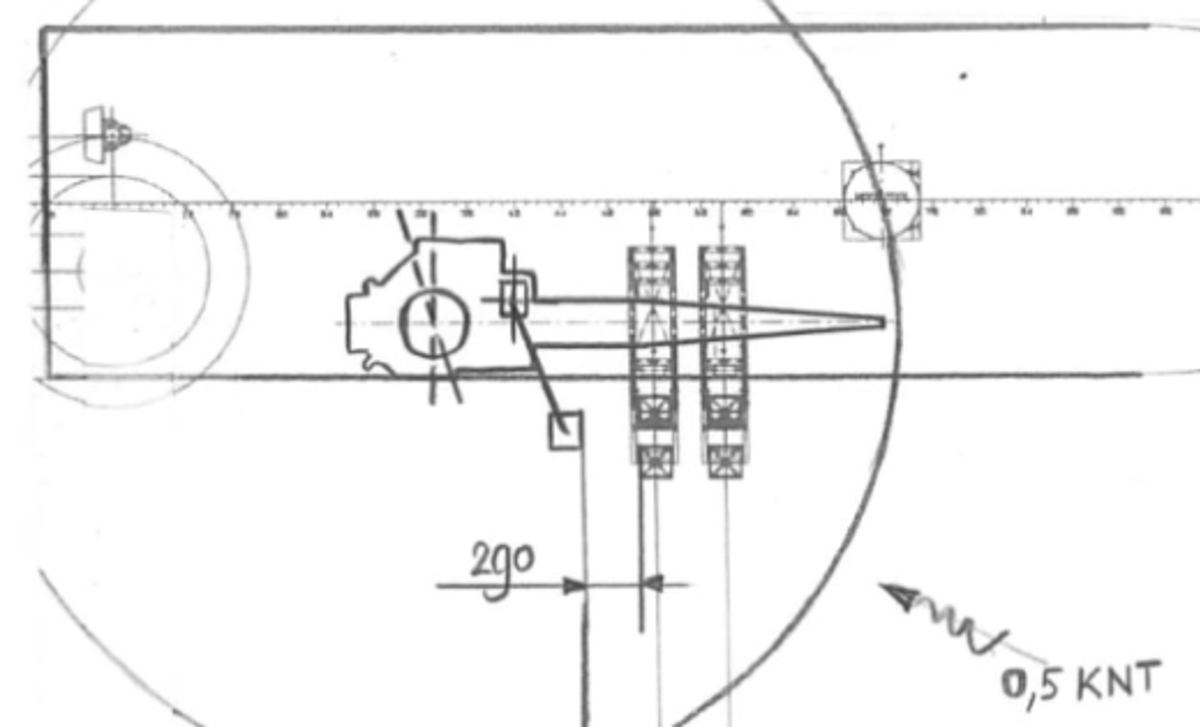
An ‘all stop’ was called, the umbilical was freed and the divers were recovered safely. The incident occurred during the recovery of two divers working from a diving basket at 22m water depth.
The divers’ umbilicals were tended from the surface through a guiding hole in the roof of the diving basket. The divers were recovered to the diving basket before recovery of the nearby tool basket, as the diving basket is considered a safe haven during lifting operations. The umbilicals were secured in the diving basket with a hold-back rope, which allowed the divers 4m of umbilical to provide length to exit the basket on deck. After the surface tenders pulled up the umbilical until they felt tension, the order was given by the supervisor to recover the tool basket to surface.

The tool basket was recovered adjacent to the diving basket using a small hydraulic crane. Just before arriving at the surface, the hold-back rope broke and the remaining 4m of umbilical started to be pulled through the guiding hole in the roof of the diving basket. When the diver noticed that he was being pulled towards the roof of the basket he immediately called an ‘all stop’. At the same time, an ‘all stop’ was also called by the tender on deck when he noticed that the umbilical was getting too close to the tool basket. The crane operator immediately stopped the crane with the tool basket approximately 2m below the surface. The snagged umbilical was visible on the tool basket. The tool basket was then lowered and the tender pulled the umbilical free. The diver had approximately 0.5m of free umbilical remaining in the basket. After the umbilical was freed, he pulled a further 3.5m of umbilical through and secured it back into the diving basket.
What went wrong? What were the causes?
- There was insufficient horizontal separation between the tool basket being recovered and the diving basket.
- the horizontal distance during lifting, between the tool basket and the diving basket, was not properly risk assessed. The distance between the crane wire and the diving basket was 2.9m on the surface during the lift which seemed sufficient at that time.
- in this case, the slack of the umbilical was pushed in the direction of the tool basket by a 0.5kt current, despite the tender pulling up and tensioning the umbilical “as normal”. The distance between the tool basket and the diving basket was known and visible at the surface but might have been different subsea.
- the crane driver did not swing the crane to maximise the distance between the lift and diving basket, as there was no proper risk assessment and associated set of instructions to do so;
- There was too much slack in the diver’s umbilical from basket to surface.
- The tool basket had protruding pins which were a snag hazard.
What lessons were learned?
Our member noted the following:
- Assure minimum distance between all lifts and umbilicals or use close observation (Diver or ROV).
- The divers were informed of the planned recovery of the tool basket, but were not informed the moment the lift actually started. Disciplined “echo” or closed-loop communications were not always applied. All operations that might affect the divers should be communicated to the divers and repeated back by the divers to the vessel to confirm the divers understanding.
- When securing an umbilical and during diver recovery, the diver is to monitor his umbilical movement interaction with the surface tender. Had he done so in this case, the diver might have noticed that his umbilical got caught by the tool basket before the hold-back rope snapped.
- The proper execution of the ‘all stop’ procedure prevented a worse outcome in this case. The ‘all stop’ was effective because the deck crew could see what was happening and because the very high frequency (VHF) channel was not occupied. Consideration should be given to dedicated communications systems.
- Smaller hydraulic cranes used to deploy tool baskets etc. may be operated on an ad hoc basis by a member of the dive team, and there may be no specific work instructions or competence schemes in place for these operations.
- Though the tender pulled on the umbilical until it was tight, he was not exactly aware of how much slack there was in the water as this depended on multiple variables; the diving umbilical is marked at 5m intervals, so the tender has an idea of the length of umbilical paid out, but for enhanced umbilical management during critical phases, the tender should be provided with additional information regarding acceptable slack in water and should be able to measure this.
What actions were taken?
- The addition of ‘operation of the auxiliary crane’ to the Vessel specific manual.
- Creation of a checklist/familiarization for an auxiliary crane operator.
- Thorough check of Diver Supervisor communications with regard to criticality and ‘fail safe’.
- Provision of detailed instruction, guidance and information on acceptable slack for the tender.
- Removed the pins creating a snagging hazard from the outside of all tool baskets in use.
Members may wish to refer to Guidance on operational communications
Related Safety Flashes
-
IMCA SF 22/16
1 September 2016
-
IMCA SF 05/16
24 February 2016
-
High potential near-miss: Failure of both divers’ breathing air supply and dive stage recovery winch
IMCA SF 01/16
7 January 2016
IMCA Safety Flashes summarise key safety matters and incidents, allowing lessons to be more easily learnt for the benefit of the entire offshore industry.
The effectiveness of the IMCA Safety Flash system depends on the industry sharing information and so avoiding repeat incidents. Incidents are classified according to IOGP's Life Saving Rules.
All information is anonymised or sanitised, as appropriate, and warnings for graphic content included where possible.
IMCA makes every effort to ensure both the accuracy and reliability of the information shared, but is not be liable for any guidance and/or recommendation and/or statement herein contained.
The information contained in this document does not fulfil or replace any individual's or Member's legal, regulatory or other duties or obligations in respect of their operations. Individuals and Members remain solely responsible for the safe, lawful and proper conduct of their operations.
Share your safety incidents with IMCA online. Sign-up to receive Safety Flashes straight to your email.